


What you need to know about
Gum Disease
Simple answers to frequently asked questions about
Gum Disease
WHAT IS PERIODONTAL DISEASE?
A disease which affects the gums and other supporting structures of the teeth is known as Periodontal disease. It is commonly known as gum disease. The early
Stage of the disease is referred to as Gingivitis and is characterised by inflammed gums which bleed easily. In the more advanced stage, the disease affects the bone and other supporting structures and is known as periodontitis.
WHAT CAUSES GUM DISEASE?
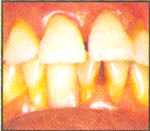
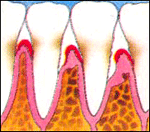
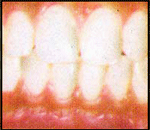
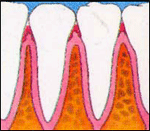
The early stage of gum disease, gingivitis, starts with plaque. Plaque is a soft, sticky colourless film of bacteria that constantly forms on teeth. If you do not clean your teeth properly, the plaque builds and enzymes that can irritate the gums. Gums can become red, swollen, sensitive and can bleed on provocation.
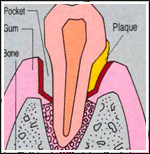
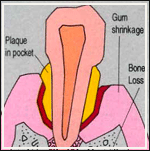
In time, the build-up of plaque can move below the gum-line. This causes an inflammation which form pockets, that is, a space between the teeth and gums. It also destroys the underlying bone. This advanced stage is known as periodontitis. As more bone gets destroyed, the tooth can loosen and eventually fall out or may need to be removed.
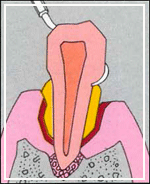
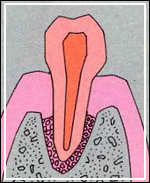
Although periodontal diseases can occur at any age, they usually affect adults. As many as 90% of people above 40 years suffer from some form of gum-disease, making it the leading cause of toothloss in adults.
HOW DO I KNOW IF I HAVE IT?
Some early warning sings of impending gum disease are:
Gingivitis Red, swollen or tender gums. Gums that bleed while brushing,
Periodontis Gums separated from your teeth. Pus between teeth and gums.
Change in the way teeth fit together. Loose or shifting teeth.
Bad breath or bad taste.
Should you notice any of the above sings and symptoms, visit your dentist immediately. It is prudent to meet your dentist at least twice a year thereafter.
HOW CAN I PREVENT GINCIV IT IS?
- The only, effective way is to prevent build-up of plaque. Brushing and flossing twice a day & after meals can control plaque build-up
- Eat a balanced diet, especially one rich in dietary fibre. Fresh fruits and vegetables, milk and fish are recommended.
- Visit your dentist at least twice a year. He is trained to recongnise early symptoms of gum disease and offer curative procedures.
SO GUM DISEASE IS CURABLE!
Yes, Early gingivitis is usually completely reversible. Your dentist will treat the disease through professional cleaning and scaling to remove plaque. You must follow that up with certain preventive measures that prevent the resettling of plaque at the gum-line:
Advanced gum disease, now referred to as periodontitis, may require surgery to help save teeth. Only very advanced stages are incurable.
HOW DO I PREVENT THE ONSET OF
GUM DISEASE IN THE FIRST PLACE!
Certain preventive measures are known to prevent the re-settling of plaque at the gum-line and therefore, reduce the risk of gum disease. You must practice these good dental habits:
BRUSHING
- Brush your teeth twice a day. Hold a soft brush at the gum line at a 45* angle. Brush in a circular motion to massage the gums and an up-down motion to dislodge plaque. Do this gently on the outer as well as inner surfaces of teeth.
- Replace your brush every 3 or 4 months.
FLOSS
Floss daily to remove plaque from between teeth. Take about 18” of floss and wrap most of it around your middle finger and the rest around the middle finger of the other hand, leaving a 2” length between them. Using your thumb and forefinger, gently scrape the side of each tooth away from the gum.
RINSE
Rinse your mouth with water thoroughly after each meal. Rinse for a minute everyday with mouthwash.
1. Prevention of gum disease is achieved by
- Regular and effective brushing
- Flossing in between teeth
- Rinsing
- All of the above
- Plaque build-up
- A damaged toothbrush
- Chewing hard foods.
- Early gingivitis and then periodontitis
- Periodontitis followed by advanced gingivitis.
1. All these
2. Plaque build-up
3. Early gingivitis followed by advanced periodontitis



